查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过





作者:南京大学神经病学研究所 刘锐
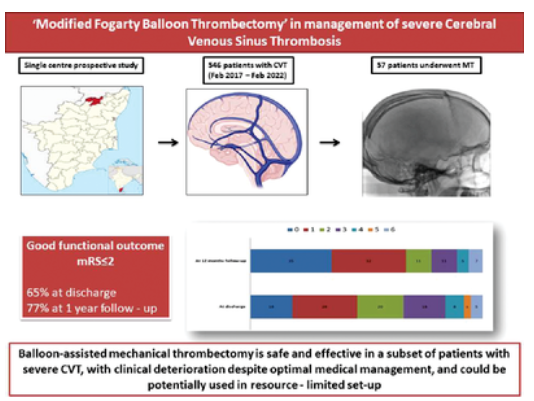
1. 临床恶化——我们将“临床恶化”定义为尽管进行了最佳的医疗管理,但出现以下任何一种或多种特征的复合终点,且排除了其他原因,如电解质紊乱、尿毒症、肝功能障碍:
(1)与入院时的评分相比,格拉斯哥昏迷评分下降(格拉斯哥昏厥评分<8或运动/言语/睁眼反应下降至少1分)
(2)恶化/新发局灶性神经功能缺损
(3)新发/复发性癫痫
2.颅内高压恶化——我们将“颅内高压恶化”定义为尽管进行了最佳医疗管理,但出现以下任何一种或多种特征的复合终点:
(1)颅内压升高的持续症状(头痛加剧、持续呕吐、心动过缓和高血压)
(2)ICU住院期间的重复成像显示静脉梗死继发的脑水肿/肿块效应恶化
3. 深静脉系统受累(直窦、盖伦静脉和大脑内静脉)
4. 全身抗凝的禁忌证,如严重血小板减少症(血小板<20000 cu mm,活动性全身出血或出血体质)
Clinical deterioration – We defined “clinical deterioration” as a composite end point of occurrence of any 1 or a combination of the following features despite optimal medical management, with other causes like dyselectrolytemia, uremia, hepatic dysfunction being excluded:
Drop in Glasgow Coma Score when compared with the score at admission (Glasgow Coma Score<8 or drop by at least 1 point in either motor/verbal/eye opening responses)
Worsening/new onset focal neurological deficits
New onset/recurrent seizures
Worsening intracranial hypertension – We defined “Worsening intracranial hypertension” as a composite endpoint of occurrence of any 1 or a combination of the following features despite optimal medical management:
Persistent symptoms of raised intracranial pressures (increased headache, protracted vomiting, bradycardia, and hypertension)
Repeat imaging during the course of ICU stay showing worsening cerebral edema/mass effect secondary to venous infarction
Involvement of deep venous system (straight sinus, vein of Galen, and internal cerebral veins)
Contraindication to systemic anticoagulation such as severe thrombocytopenia (platelets <20 000cu mm, active systemic bleeding or bleeding diathesis)

来源:第67病区
相关推荐
酗酒者癫痫发作的亚急性脑病(SESA综合征)1例报告及文献复习
查看更多