查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过






Stroke & Vascular Neurology(SVN)最新上线文章“Neglected Mendelian causes of stroke in adult Chinese patients who had an ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack”,来自首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院、首都医科大学卒中精准临床诊疗与研究中心王拥军教授团队。

多种因素在卒中的发生及预后中发挥着重要作用,然而,单基因变异在全因缺血性卒中的作用尚未得到系统研究。作者团队旨在基于成人缺血性卒中/短暂性脑缺血发作(TIA)队列(第三次中国国家卒中登记,CNSR-Ⅲ)识别漏诊的单基因卒中。
对CNSR-Ⅲ招募的10428例患者的DNA样本进行181个与卒中相关基因的靶向二代测序。审查电子健康记录(EHRs)中的遗传和临床数据以完成诊断过程。作者团队评估了具有致病性或可能致病性(P/LP)变异的个体的百分比,以及具有相关表型的已知单基因疾病基因中致病性变异的诊断率。
研究结果显示,10428例患者中共有1953例携带至少一种P/LP变异。792例(7.6%)个体根据遗传模式预测具有患一种或多种单基因疾病的风险,其中,759例个体在单个基因中携带一种P/LP变异,29例个体在不同基因中携带两种或多种P/LP变异,4例个体在ABCC6中携带两种P/LP变异。792例患者中230例在EHR数据中表现出临床表型,支持单基因病因卒中的诊断。该队列中诊断最多的孟德尔卒中病因是伴有皮质下梗死和白质脑病的常染色体显性遗传性脑动脉疾病。年龄或家族史与患者首次症状性单基因卒中的发生率之间没有关系。
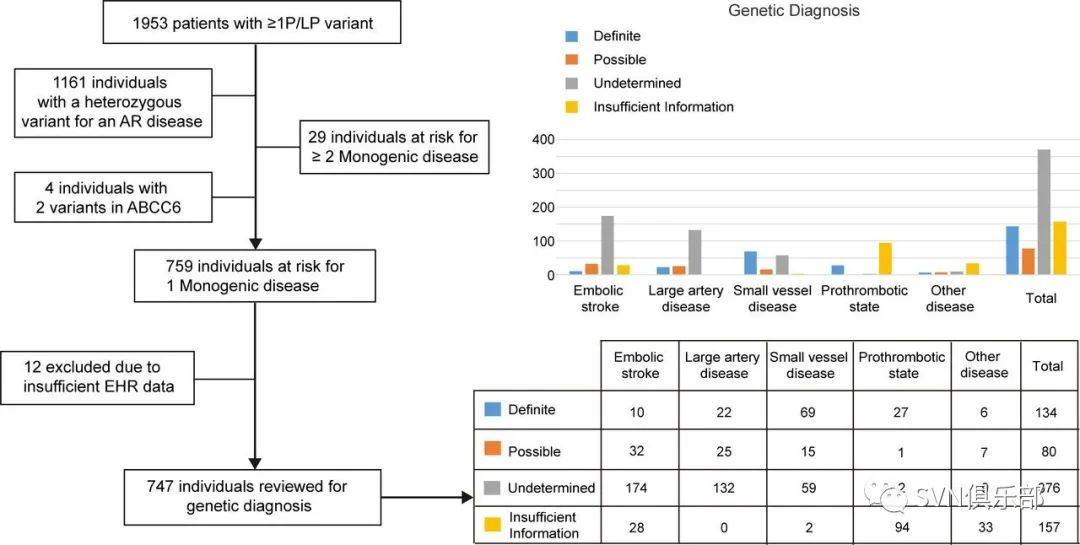
Figure 2. Individuals diagnosed and potentially missed diagnoses. Flow chart (left) illustrating the number of individuals harbouring one or more P/LP variant, and the number of individuals predicted to develop one or more monogenic disease. Bar plot (right) illustrating the proportions of the groups at risk for one monogenic disease, showing their likelihood of a missed diagnosis.
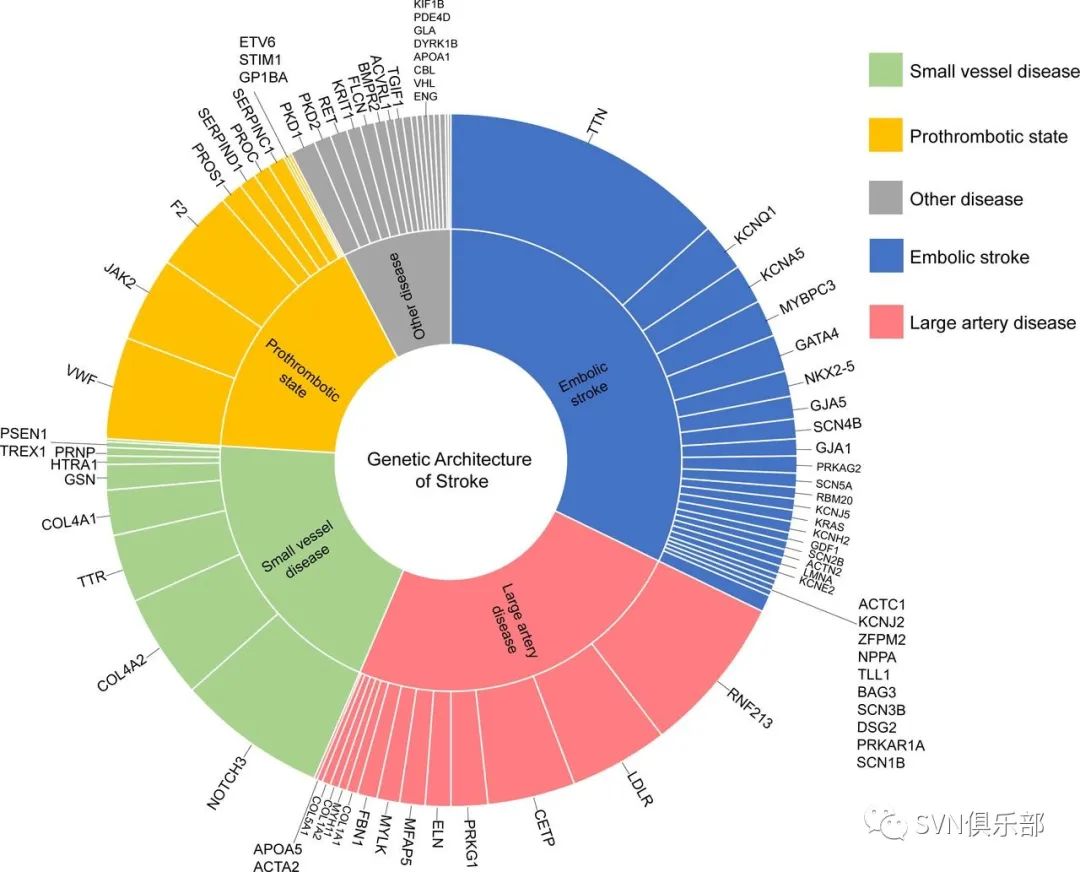
Figure 3. Genetic architecture of stroke. Each gene related to monogenic stroke identified in 759 individuals was classified into five subgroups: large-artery disease, small-vessel disease, embolic stroke, a prothrombotic state and other diseases (shown in the middle text circle). The proportions of affected genes are shown in the outermost circle.
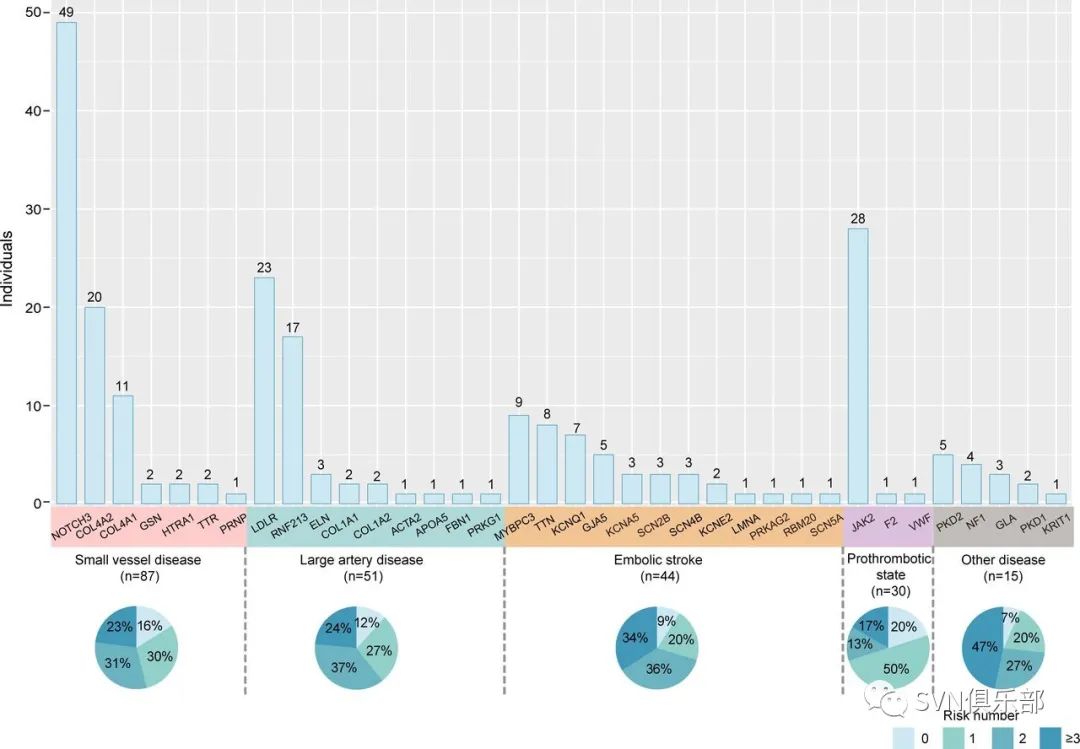
Figure 4. Characteristics of 227 individuals diagnosed with Mendelian causes of stroke. The bars represent the number of individuals diagnosed with Mendelian causes of stroke identified for each gene, which are coloured according to the classification of stroke aetiology. Three individuals with two monogenic diseases were ruled out. The percentages in the boxes indicate the distribution of risk factors, including hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes, coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, smoking history, drinking history and body mass index ≥25.
回顾临床表型,单基因卒中发生率为2.2%。在缺血性卒中/TIA成年患者中,孟德尔卒中病因可能被漏诊的潜在原因包括卒中症状晚发、常合并常见血管风险以及缺乏显著的家族病史。

来源:SVN俱乐部
转载已获授权,其他账号转载请联系原账号
国家神经系统疾病质控中心脑血管病专业组专家撰稿,21篇脑梗死临床诊疗干货文章,精准提升脑血管临床诊疗能力!
华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院杨渊教授团队撰写17篇神经心理疾病临床干货文章,神经内科医生需要了解!
国家神经系统疾病质控中心帕金森病专家组倾力打造,2023年度帕金森病规范诊治能力提升培训!
脑血管病影像读图实战训练,跟随天坛医院放射科沈宓老师,练就影像读图火眼金睛!
躯体症状障碍的识别、评估及治疗丨17天神经心理疾病诊治突破⑦
查看更多