查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过





作者:南京大学神经病学研究所 刘锐

doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-017693. Epub 2021 Jun 29.
CASE SUMMARY
A male patient in his late 50s who had untreated atrial fibrillation received mechanical thrombectomy for right middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCA), with complete recanalization.
一名50多岁的男性患者患有未治疗的心房颤动,接受了右侧大脑中动脉闭塞(MCA)机械取栓术,并实现了完全再通。
After initial neurological improvement, he developed headache and altered vigilance 2 days post-thrombectomy.
在初步神经系统改善后,患者在取栓后2天出现头痛和意识水平下降。
Transcranial duplex sonography (TCD) showed increased blood flow velocities in the entire ipsilateral (recanalized) MCA-M1 segment.
TCD)显示整个同侧(再通)MCA-M1节段血流速度增加。
Brain MRI with angiography excluded focal stenosis and showedvasogenic edema, hemorrhagic transformation of the ischemic infarct, and cerebral hyperperfusion in the right MCA territory .
MRI和血管造影排除局灶性狭窄,显示血管源性水肿、缺血性梗死的出血性转化和右侧MCA区域的脑高灌注。
Because of this finding, the patient underwent intense blood pressure (BP) control (systolic BP target <140 mmHg). MCA flow normalized in the following days and the patient clinically improved. At 3 months after the stroke, functional neurological outcome was favorable (modified Rankin Scale score 2).
由于这一发现,患者接受了高压血压控制(收缩压目标<140 mmHg)。在接下来的几天内,患者的MCA血流恢复正常,临床情况有所改善。卒中后3个月,神经功能预后良好(修正Rankin量表评分2分)。
Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome is a wellknown complication after stenting/surgery of longstanding carotid artery stenosis and can lead to brain edema and hemorrhage, and poor outcome if not treated properly (ie, BP control).
脑高灌注综合征是长期颈动脉狭窄的支架植入/手术后常见的并发症,可导致脑水肿和出血,如果治疗不当(即血压控制),预后不良。
Although the exact pathophysiology still has to be elucidated, impaired cerebral autoregulation is the most probable underlying mechanism of cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome.
虽然确切的病理生理机制尚未阐明,但大脑自调节功能受损是脑高灌注综合征最可能的潜在机制。
Other mechanisms that have been implicated are formation of reactive oxygen species with consecutive damage of the cerebrovascular endothelium,baroreceptor reflex breakdown, or trigeminovascular reflex dysregulation.
其他相关的机制包括脑血管内皮连续损伤的活性氧的形成、压力感受器反射崩溃或三叉血管反射失调。
Recently, increased MCA blood flow velocities were observed on TCD in individual patients after stroke thrombectomy and were associated with intracranial hemorrhage.
最近,在脑卒中血栓切除术后的个别患者TCD上观察到MCA血流速度增加,并与颅内出血有关。
However, the retrospective study design did not allow elucidation of the exact mechanism underlying increased TCD flow velocities in the recanalized MCA (hyperperfusion vs localized vasospasm/vessel stenosis).
然而,回顾性研究设计不能阐明再通MCA中TCD血流速度增加的确切机制(高灌注vs局部血管痉挛/血管狭窄)。
The present case illustrates classic clinical (headache/altered vigilance) and neuroimaging features (vasogenic edema/hemorrhage) of cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after stroke thrombectomy and clearly demonstrates the concordance of postinterventional hemodynamic findings on TCD and perfusion MRI. Therefore, TCD could be regarded as a valuable bedside tool to screen for this important complication after stroke thrombectomy
本病例展示了脑卒中取栓术后脑高灌注综合征的经典临床(头痛/警觉性改变)和神经影像学特征(血管源性水肿/出血),并明确显示了介入后TCD和灌注MRI血流动力学结果的一致性。因此,TCD可作为筛查脑卒中取栓后这一重要并发症的一种有价值的床头工具。
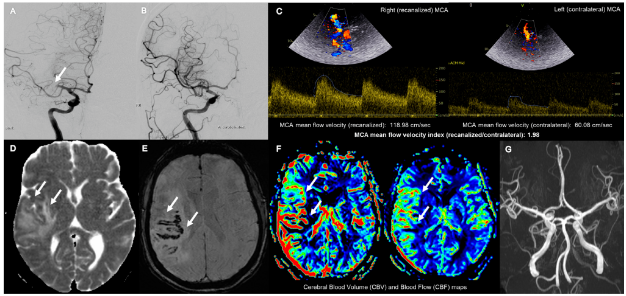
TCD、MRI以及DSA显示取栓后高灌注综合征,右侧大脑中动脉(MCA)闭塞(A,箭头)。机械取栓可成功实现再通(脑梗死溶栓3);B).TCD检测到再通的右侧MCA血流速度增加(与对侧相比;C)取栓后2天。脑MRI在视弥散系数图上显示血管源性水肿(D,箭头),在敏感性加权成像上显示出血性转变(E),在灌注加权成像上证实高灌注(F)。MRA造影排除颅内血管狭窄或血管痉挛(G)。
来源:第67病区
二甲双胍、碘过敏……CT、CTA等检查前需要有哪些注意事项?
徐运:缺血性卒中个体化抗血小板治疗及评估丨CSA&TISC2022
急性脑出血患者收缩压 180 mmHg,紧急降至多少才安全?
ISC 2022|续写新篇章 —— “替奈普酶”精彩继续……
神经影像问答:脑干梗死后华勒氏变性(WD)有什么影像特点和临床表现?
查看更多