查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过





基本资料
Male, 55 yo, Hepatitis B virus (+), Cirrhosis
2008, sHCC(1cm), 4 times TACE, normal AFP
TACE: 2009.1, 2009.4, 2010.1, 2011.8
2014.12 HCC recurrence, AFP 41ng/ml
2015.2.15 Orthotopic Liver Transplant (piggy back)
Liver function: Child C
辅助检查
Pathology:
Cirrhosis, far advanced HCC (10cm, LL)
Portal vein tumor thrombosis (Vp3)
Moderate-poor differentiation
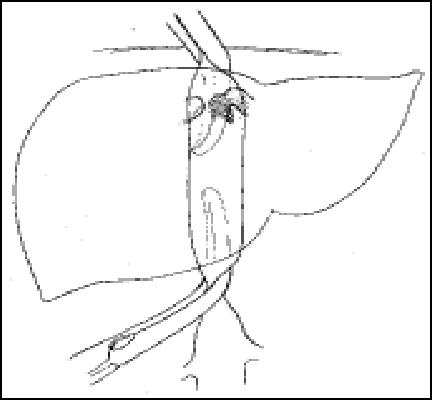
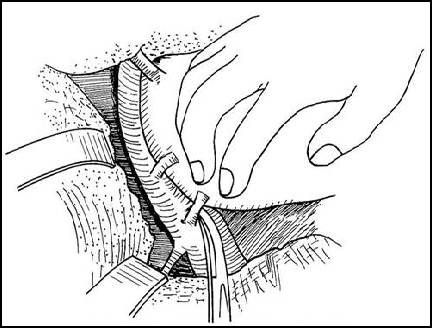
“no touch” technique
Total Hepatectomy
-Clamping infrahepatic vena cava
-Clamping suprahepatic vena cava
-Mobilize the liver
-Remove the diseased liver
Benefits & advantages
-Reduce intraoperative hemorrhage
-Reduce risk of pulmonary embolism
-Reduce the risk of tumor metastasis
Customized Immunosuppression
POD immunosuppressant:
-Steroid-free (1000mg intraoperative) regimen
-Induction with IL2RA (basiliximab 20mg on POD 0&4), delaying Tac initiation by 3-5 days
-Low dose Tac (Through 6-10ng/ml within 3 months, 6-12 months 3-5ng/ml, beyond 12 months less than 3ng/ml)
-Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1000mg BID
Post-transplant management
-2015.8.31 Lung metastasis (1.5cm, right)
-Video-assisted thoracoscopic wedge resection
-Pathology: poorly differentiated metastatic tumor
-2016.8.3 Lung metastasis (multiple, bilateral)
-3 times of mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy
mFOLFOX6:奥沙利铂130mg d1+CF 700mg d1+5-FU 3500mg civ 46h Q2W
Date: 2016-09-12、2016-9-26、2016-10-10
-1 time of GS chemotherapy
GS :吉西他滨1.8g d1+替吉奥60mg bid d1-7
Intolerance: III°骨髓抑制,不能耐受停用
-TKI: Sorafenib 400mg BID
PD
-2016.12.19 Immunotherapy (NK cell)
2 times of NK cell therapy
Injection of 6.4 × 109 NK cells for 3 days
Date: 2016.12.19-2016.12.21; 2017.1.1-2017.1.3
-1 time of bronchial artery chemoembolization
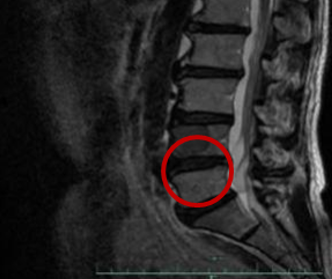
-2017.9.29: T3, T4 bone metastasis
唑来膦酸Zoledronic acid
SD→PD
-2017.10.6-2019.4.9 Immunotherapy (PD-1 inhibitor)
Opdivo 200mg Q2W x 31 times
Date: 2017-10-6,2017-10-20,2017-11-03,2017-11-21,2017-12-06,2017-12-20,2018.01.04,2018.1.18,
2018-2-3,2018.2.20,2018.03.06,2018-03-20,2018-04-04,2018.4.17,2018.5.2,2018-5-17,2018.6.5,
Initial: Sorafenib 400mg BID
PD
2018-6-21,2018-7-12,2018-8-3,2018.9.13,2018.9.28,2018.10.11, 2018.10.31,2018.11.20,2018-12-13,
Intolerance
2019-1-4,2018-01-24,2019-2-22,2019-03-15,2019-04-09
Pleural effusion
-TKIs
2018.3.19 Regorafenib 80mg qd
2018.3.26 Anlotinib 12mg qd D1-14 q3w
2019.2.22 Apatinib 250mg qd
2019.3.6 Levatinib 8mg qd
SD, no rejection
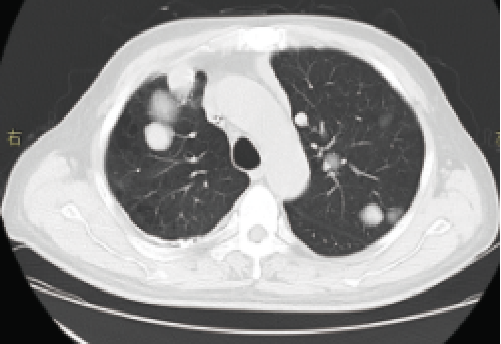
One month before treatment
September 2017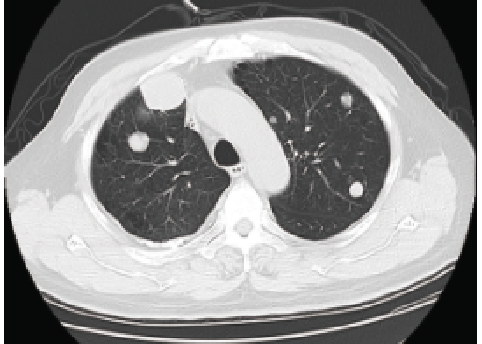
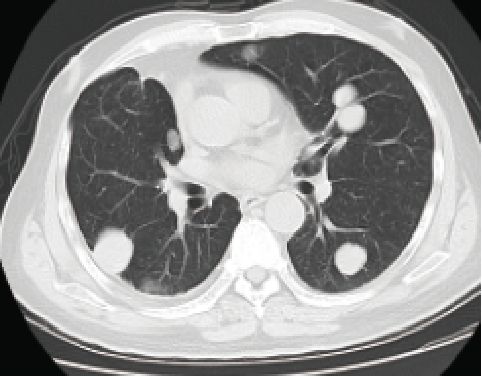
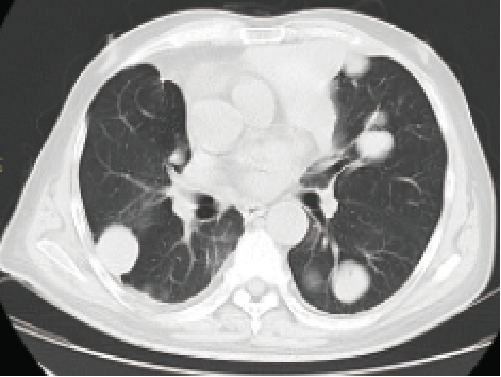
One year after treatment
September 2018
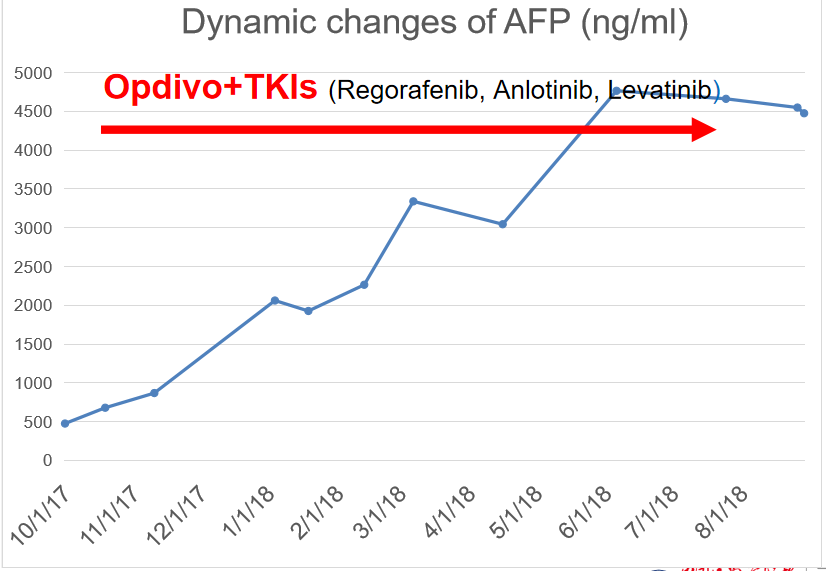
Biological response: AFP
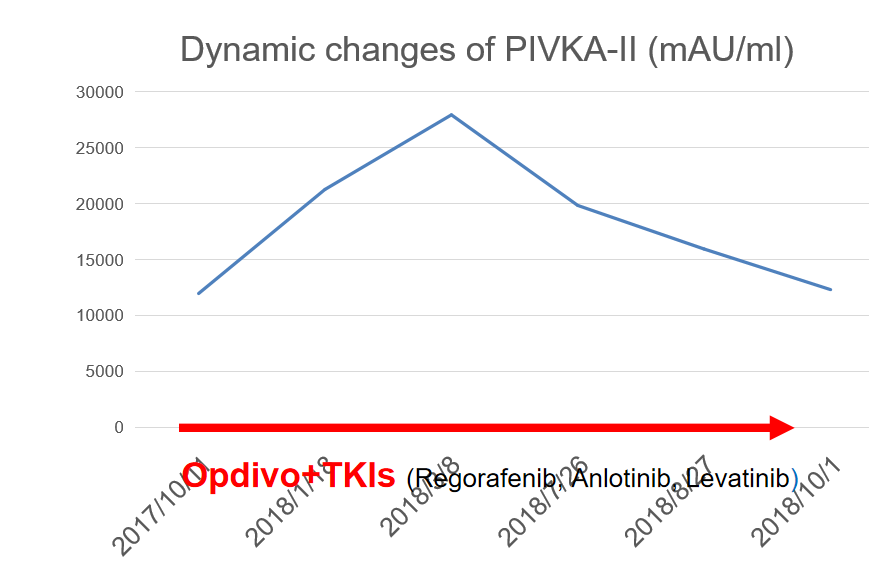
Biological response: PIVKA-II
Summary of treatment with ICIs for recurrent HCC

DISCUSSION
Liver 15–40% Extrahepatic 50–60%
Liver + Extrahepatic 30–40%
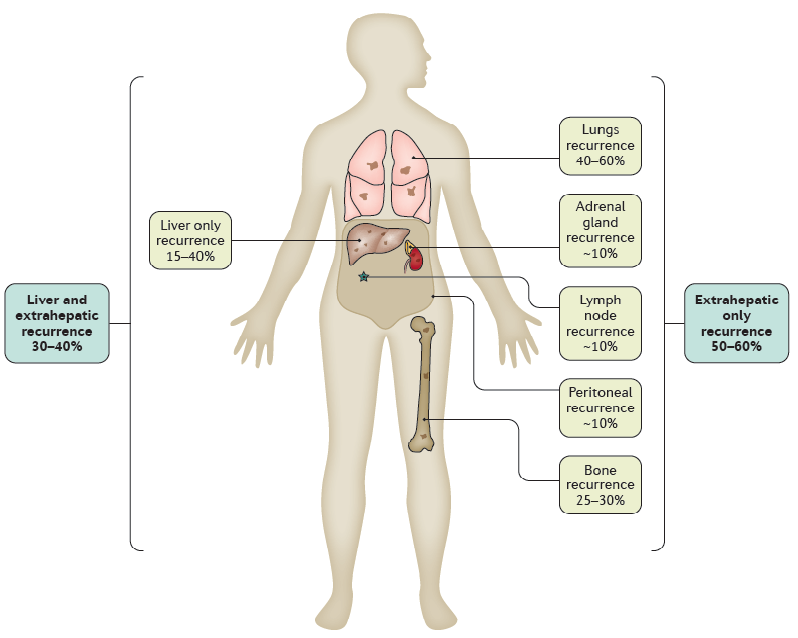

Lung metastasis 40~60%
Bone metastasis 25~30%
Management of Recurrent HCC:
Hangzhou experience
Data from our center (293 HCC, 64 pts recurrence) (2016.1.1-2017.12.31)
Treatment modality for recurrence %
Surgery: 15/64 (23.4%)
TACE: 14/64 (21.9%)
RFA: 6/64 (9.4%)
Systematic chemotherapy: 32/64 (50%)
Molecular targeted therapy (sorafenib,
regorafenib, lenvatinib, apatinib): 33/64 (51.6%)
External beam radiation: 5/64 (7.8%)
Immunotherapy (PD-1 inhibitor): 3/64 (4.7%)
Best supportive care: 9/64 (14.1%)
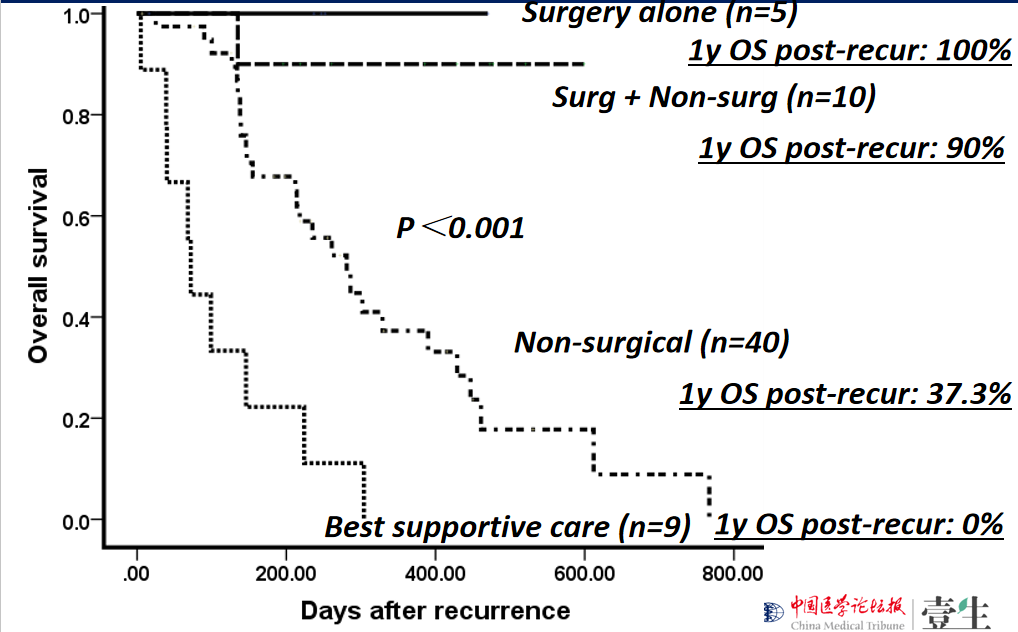
Recurrent HCC treatment:
surgical treatment is the priority
TKIs for advanced HCC

Sorafenib as the First-line
systemic treatment
PFS: ≈ 1 y
Combinated with immunotherapies such as: NK cell, PD-1 inhibitor
索拉非尼耐药后瑞戈非尼序贯治疗
Retrospective, multicentre, international study
索拉非尼耐药后瑞戈非尼序贯治疗: 肝癌肝移植术后肿瘤复发患者总体生存时间平均延长38.4个月

肝癌的免疫治疗疗效


局部治疗+免疫治疗/靶向治疗的联合
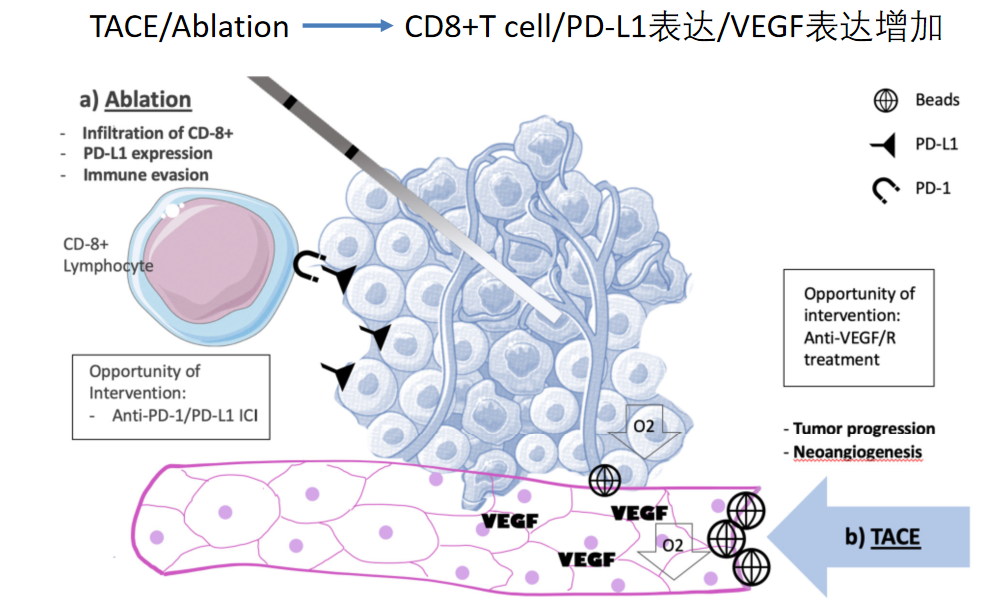
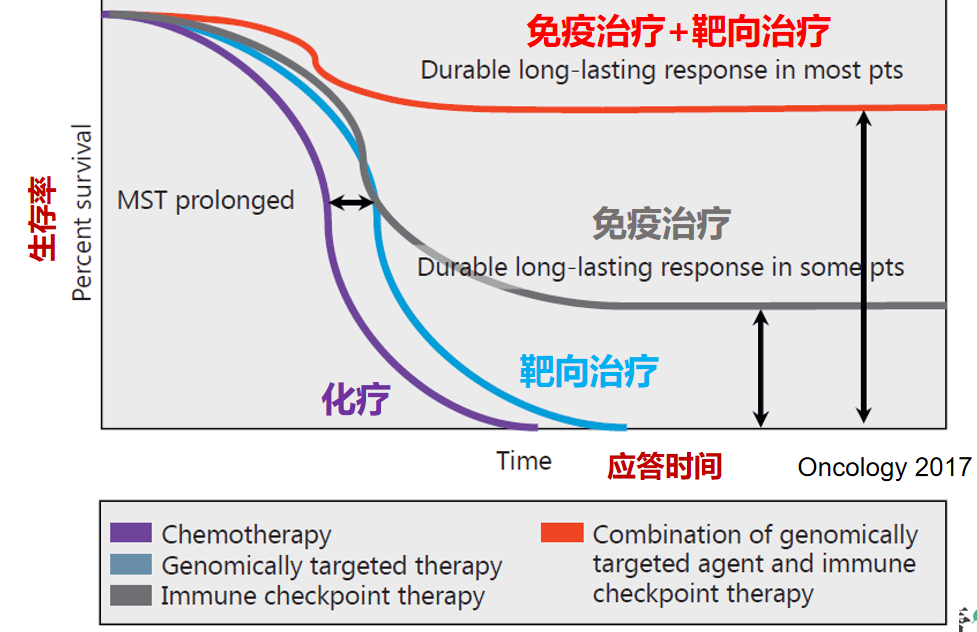
TKIs+ICIs: long-lasting response
SUMMARY

查看更多