查看更多
密码过期或已经不安全,请修改密码
修改密码
壹生身份认证协议书
同意
拒绝

同意
拒绝

同意
不同意并跳过






Stroke & Vascular Neurology(SVN)最新上线文章“Residual inflammatory risk predicts long-term outcomes following stenting for symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis”,来自首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院介入神经病学科马宁教授团队。

残余炎症风险(Residual inflammatory risk, RIR)可预测轻型缺血性卒中患者不良结局。然而,对于接受支架置入术的症状性颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄(symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis, sICAS)患者,术前RIR对长期结局的影响尚有待研究。
这项回顾性、单中心队列研究对接受颅内支架置入术的重度sICAS连续患者进行了评估。根据术前高敏C反应蛋白(high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, hs-CRP)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C)将患者分为4组:残余胆固醇炎症风险(residual cholesterol inflammatory risk, RCIR; hs-CRP≥3 mg/L, LDL-C≥2.6 mmol/L),RIR(hs-CRP≥3 mg/L, LDL-C<2.6 mmol/L),残余胆固醇风险(residual cholesterol risk, RCR; hs-CRP<3 mg/L, LDL-C≥2.6 mmol/L),以及无残余风险(no residual risk, NRR; hs-CRP<3 mg/L, LDL-C<2.6 mmol/L)。长期临床结局包括复发性缺血性卒中和死亡。长期影像学结局包括支架内再狭窄( in-stent restenosis, ISR)和支架置入后症状性ISR(sISR)。
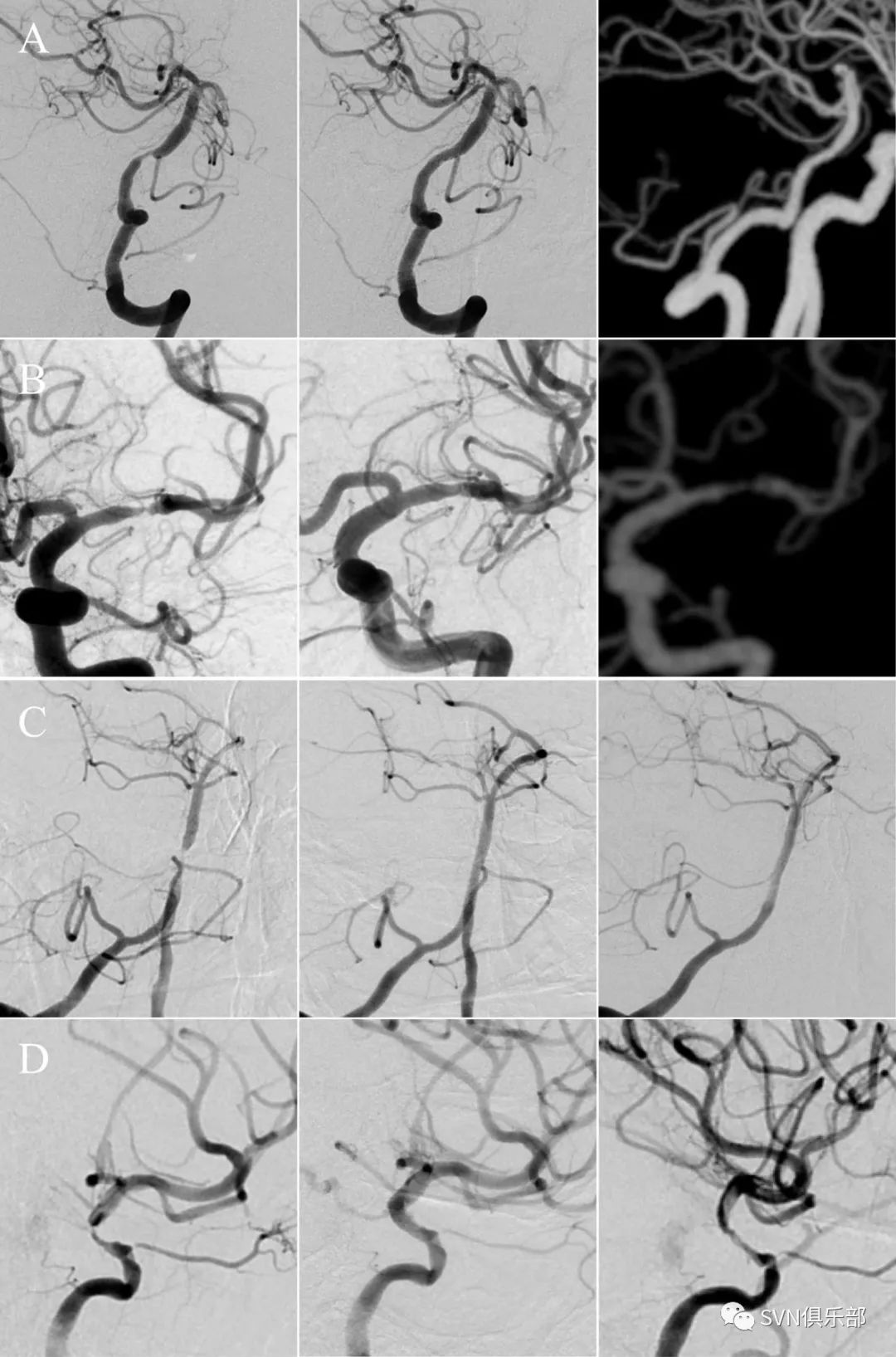
Figure 1. (A) DSA shows a 75% stenosis of BA (left) and a 10% residual stenosis after (middle) stenting. Follow-up CTA (right) after 11 months of the procedure shows no ISR. (B) DSA shows an 80% stenosis of left MCA (left) and a 25% residual stenosis after (middle) stenting. Follow-up CTA (right) after 10 months of the procedure shows ISR. (C) DSA shows an 85% stenosis of BA (left) and a 5% residual stenosis after (middle) stenting. Follow-up DSA (right) after 12 months of the procedure shows no ISR. (D) DSA shows an 80% stenosis of C7 segment of left ICA (left) and a 20% residual stenosis after (middle) stenting. Follow-up DSA (right) after 7 months of the procedure shows ISR.
研究共纳入952例患者,其中男性751例(78.9%)。残余胆固醇炎症风险(RCIR)组46例,残余炎症风险(RIR)组211例,残余胆固醇风险(RCR)组107例,无残余风险(NRR)组588例。RCIR(校正后HR 6.163; 95%CI 2.603 to 14.589; p<0.001)和 RIR(校正后HR 2.205; 95%CI 1.294 to 3.757; p=0.004)患者复发缺血性卒中风险高于NRR患者。中位随访时间为54个月。与NRR组相较,RCIR组患者(校正后HR 3.604; 95%CI 1.431 to 9.072; p=0.007)更容易发生ISR,RIR组患者发生sISR的风险显著增加(校正后HR 2.402; 95%CI 1.078 to 5.351; p=0.032),中位影像随访时间为11.9个月。
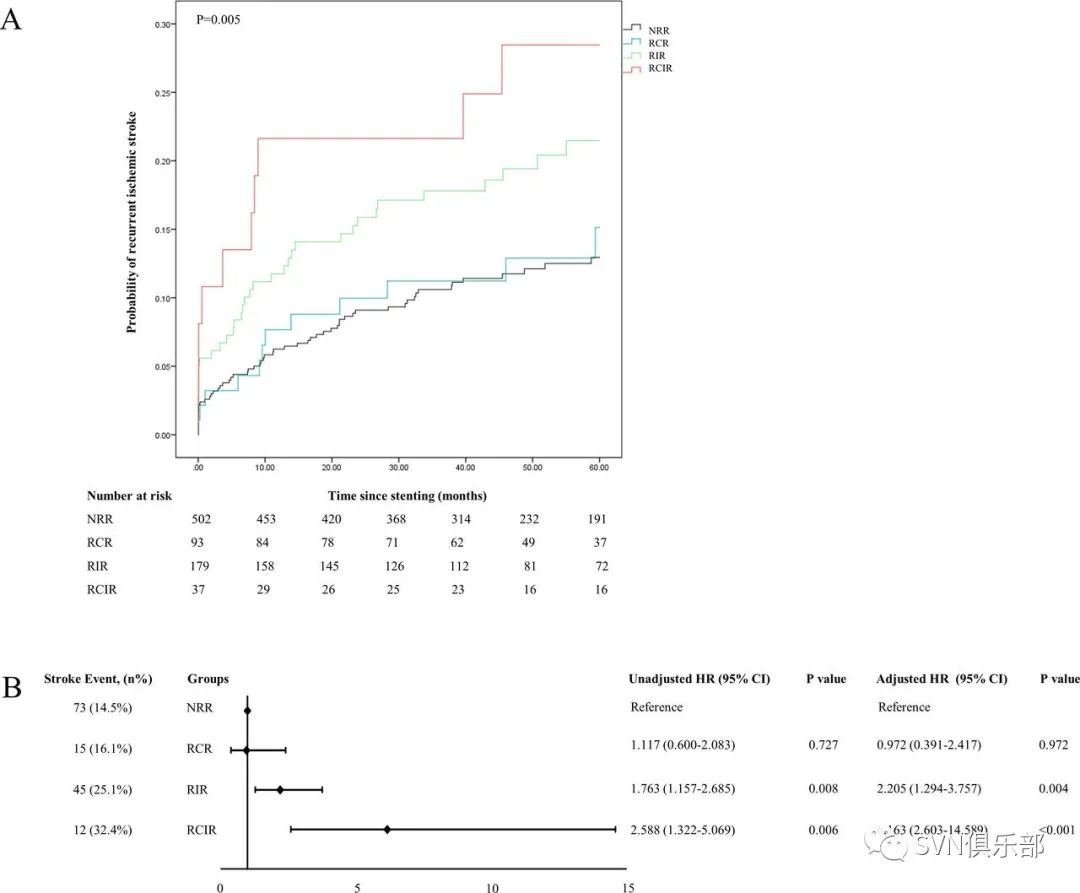
Figure 3. (A) The Kaplan-Meier survival curve for probability of recurrent ischaemic stroke within 60 months. (B) Hazard of recurrent ischaemic stroke compared with NRR. Age (>60 or ≤60 years), gender, body mass index (>28 or ≤28 kg/m2), hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolaemia, coronary artery disease, smoking, baseline NIHSS (>3 or ≤3), baseline HDL-C level (≥1.03 mmol/L or <1.03 mmol/L13), periprocedural use of Tirofiban, lesion location and LDL-C during follow-up (≥1.81 mmol/L or <1.81 mmol/L) were adjusted in the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model.
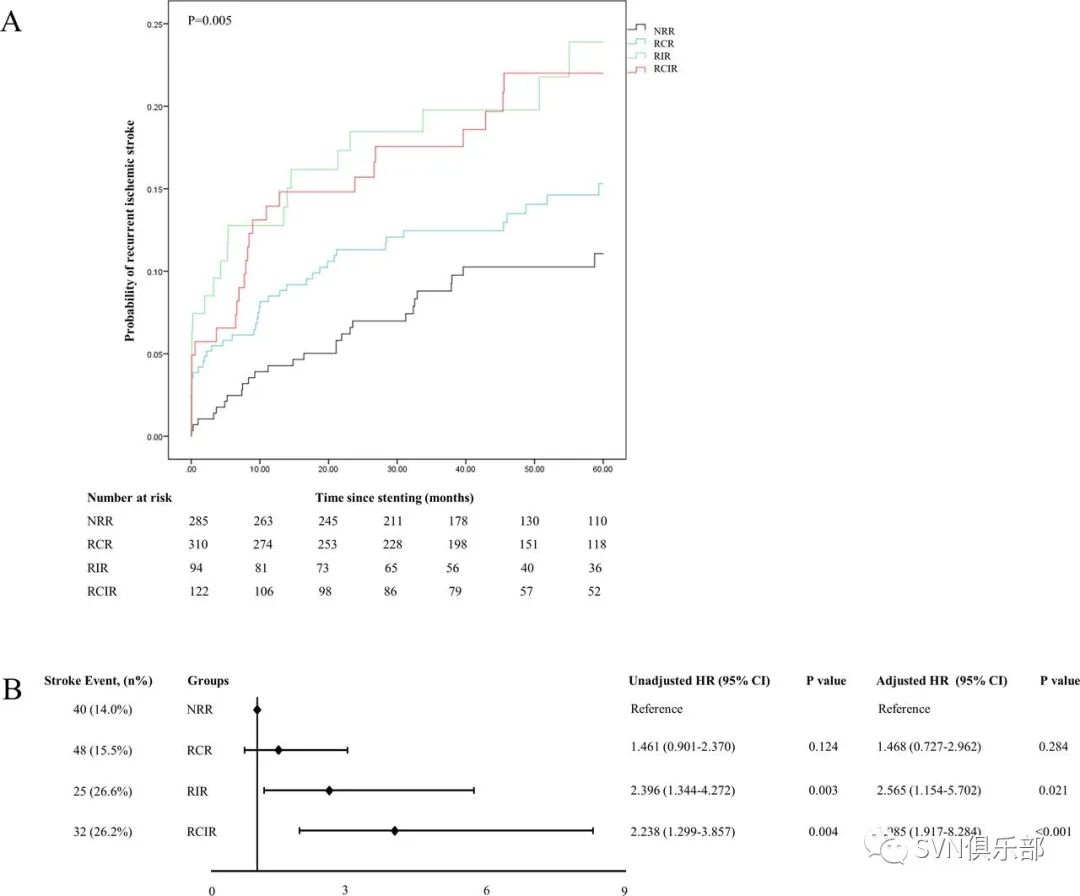
Figure 4. (A) the Kaplan-Meier survival curve for probability of recurrent stroke within 60 months by using a target cut-off level of 1.8 mmol/L for LDL-C. (B) Hazard of recurrent ischaemic stroke compared with NRR. Age (>60 or ≤60 years), gender, body mass index (>28 or ≤28 kg/m2), hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolaemia, coronary artery disease, smoking, baseline NIHSS (>3 or ≤3), baseline HDL-C level (≥1.03 mmol/L or <1.03 mmol/L), periprocedural use of Tirofiban, lesion location and LDL-C during follow-up (≥1.81 mmol/L or <1.81 mmol/L) were adjusted in the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model.
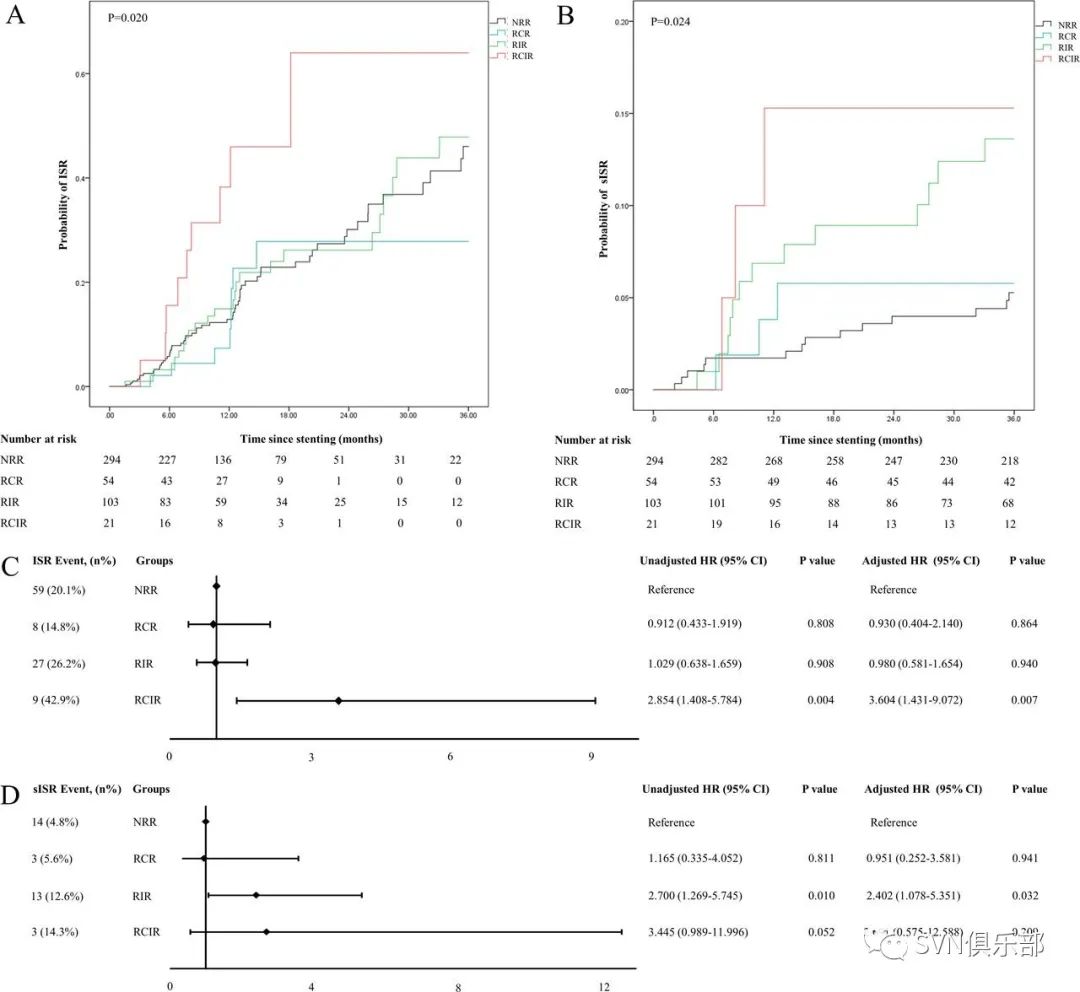
Figure 5. (A) The Kaplan-Meier survival curve for probability of ISR within 36 months. (B) The Kaplan-Meier survival curve for probability of sISR within 36 months. (C, D) Hazard of ISR or sISR compared with NRR. Age (>60 or ≤ 60 years), gender, body mass index (>28 or ≤28 kg/m2), hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolaemia, coronary artery disease, smoking, baseline NIHSS (>3 or ≤3), baseline HDL-C level (≥1.03 mmol/L or <1.03 mmol/L), periprocedural use of Tirofiban, lesion location and LDL-C during follow-up (≥1.81 mmol/L or <1.81 mmol/L) were adjusted in the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model.
研究结论,在症状性颅内动脉粥样硬化性狭窄患者中,术前RIR或可预测颅内支架置入术后长期复发性缺血性卒中、支架内再狭窄及症状性支架内再狭窄。

来源:SVN俱乐部
转载已获授权,其他账号转载请联系原账号
国家神经系统疾病质控中心脑血管病专业组专家撰稿,21篇脑梗死临床诊疗干货文章,精准提升脑血管临床诊疗能力!
华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院杨渊教授团队撰写17篇神经心理疾病临床干货文章,神经内科医生需要了解!
国家神经系统疾病质控中心帕金森病专家组倾力打造,2023年度帕金森病规范诊治能力提升培训!
脑血管病影像读图实战训练,跟随天坛医院放射科沈宓老师,练就影像读图火眼金睛!
专家共识 | 急性缺血性卒中替奈普酶静脉溶栓治疗中国专家共识
查看更多